Diabetes and Neuropathy
Neuropathy occurs when one or more nerves are damaged or destroyed. This disrupts the nerves’ ability to send messages from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, skin, and other parts of the body resulting in muscle weakness, numbness, and pain in the affected area. Frequently neuropathy begins in your hands and feet but can occur in other parts of your body as well.
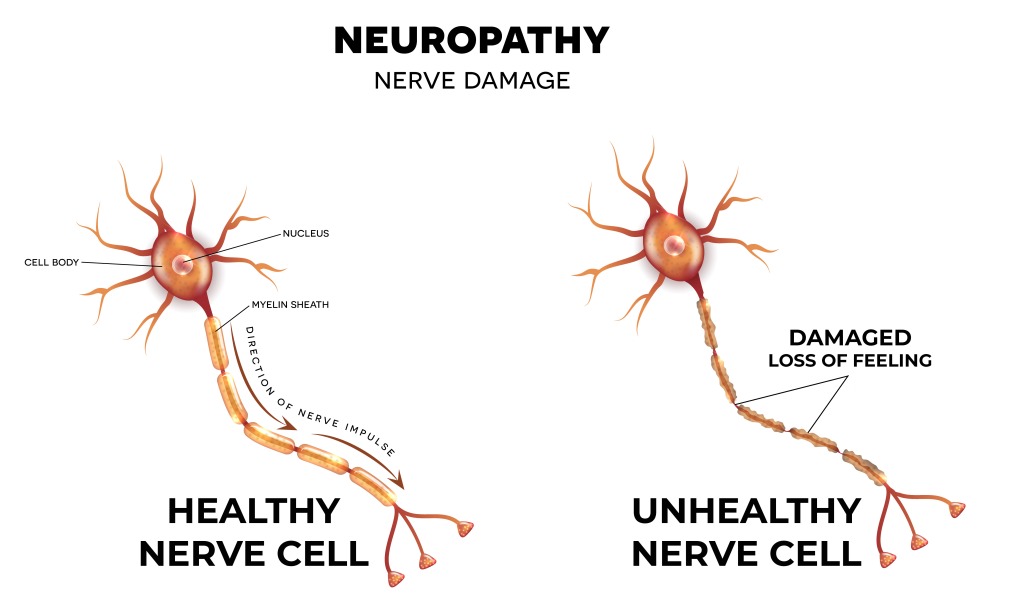
Diabetes is the leading cause of neuropathy in the United States among other causes. In fact, it is estimated that 60-70% of people with diabetes experience neuropathy. Some may experience mild symptoms, but for others, the pain can be debilitating. If you have diabetes, you can prevent or delay neuropathy by keeping your diabetes under control.
- Manage Your Blood Glucose Level
- Frequently Check Your Skin and Feet for Cuts or Sores
- Wash Your Feet Daily and Moisturize
- Wear Properly Fitted Shoes that Protect Your Toes
- Protect Your Feet and Fingers from the Heat and Cold
How Can Therapy Help?
Treatment for neuropathy is often focused on managing the underlying cause and relieving symptoms. Physical Therapy treatment may be focused on maintaining and improving function through range-of-motion exercises and stretching, strength training, balance training, and pain management. Occupational Therapy treatment can help provide education on fall prevention as well as strategies to reduce pain and increase mobility.
Source: Cleveland Clinic, The Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy, Mayo Clinic Foundation







As a physician specializing in neuropathy, I appreciate the emphasis on managing the underlying cause and relieving symptoms of neuropathy. However, it is important to note that neuropathy can also be caused by factors beyond diabetes, such as autoimmune diseases, infections, and hereditary conditions. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms of neuropathy to undergo a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause, as this can inform the most effective treatment plan. Additionally, while physical and occupational therapy can be beneficial in managing symptoms and improving function, it is important to address any underlying medical conditions to effectively manage neuropathy in the long term.