Swallowing is a complex process that involves over twenty-five muscles all working together to move food from the mouth to the stomach. For many older adults, swallowing can become a challenge.
Swallowing disorders, also known as dysphagia, can greatly impact our ability to enjoy meals and stay properly hydrated. If you find eating or drinking feels hard, experience symptoms such as coughing, choking, or feeling of food being stuck – you might be dealing with dysphagia.
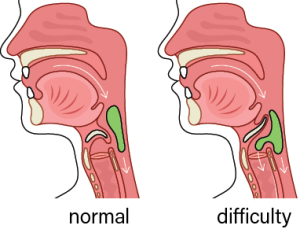
Here are some common signs that may indicate you have a swallowing problem:
• Frequent coughing or choking while eating or drinking
• A feeling of food or liquid getting stuck in your throat or chest
• Pain or discomfort in your throat or chest when swallowing
• Unintentional weight loss or dehydration
• Recurrent respiratory infections or chest congestion
How Can Speech Therapy Help?
Speech-Language Pathologists (SLP) are uniquely qualified to help people who are experiencing problems with eating and drinking. During treatment, a SLP may recommend swallowing exercises along with other strategies to help manage dysphagia. If you or a loved one experience difficulty swallowing, talk to your doctor about Speech Therapy. Early identification and treatment of swallowing problems can help prevent complications and improve your quality of life.





